National Railway Museum, Delhi, India, 26/12/1993
Photographs of various locomotives at the National Railway Museum in Delhi.
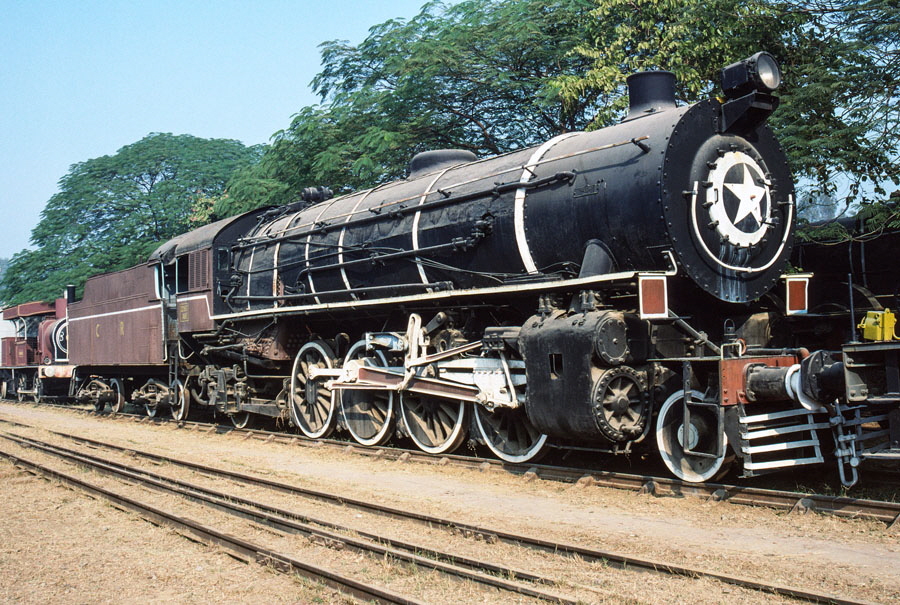

1-of-12) Broad gauge, IRS (Indian Railway Standard) class AWE 2-8-2 22907.
This locomotive was built by Baldwin, in the U.S.A., in 1943.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
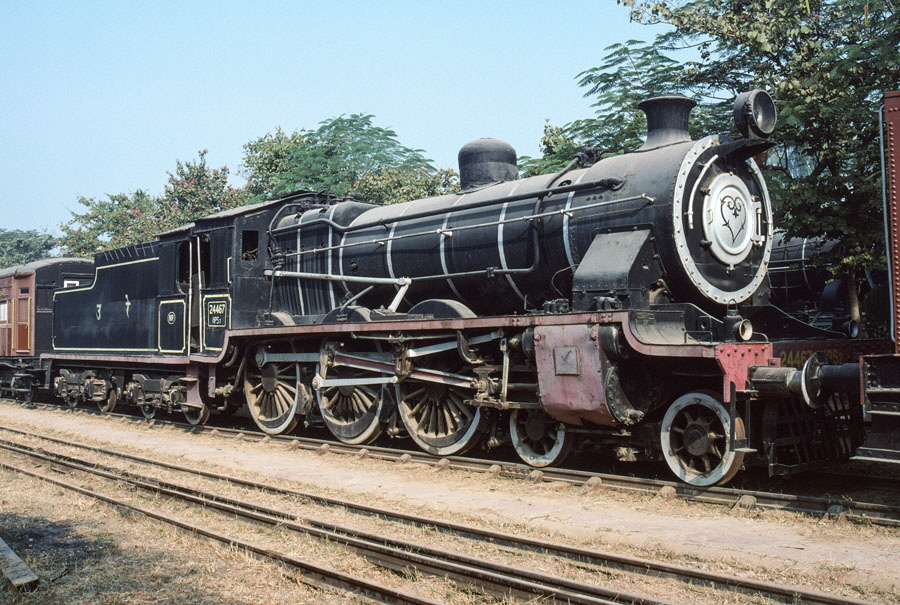

2-of-12) Broad gauge, class HPS/2 4-6-0 24467.
This classic Indian “Mail Engine”, originating from a BESA (British Engineering Standards Association) design of 1906, was built by Vulcan Foundry as late as 1950.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
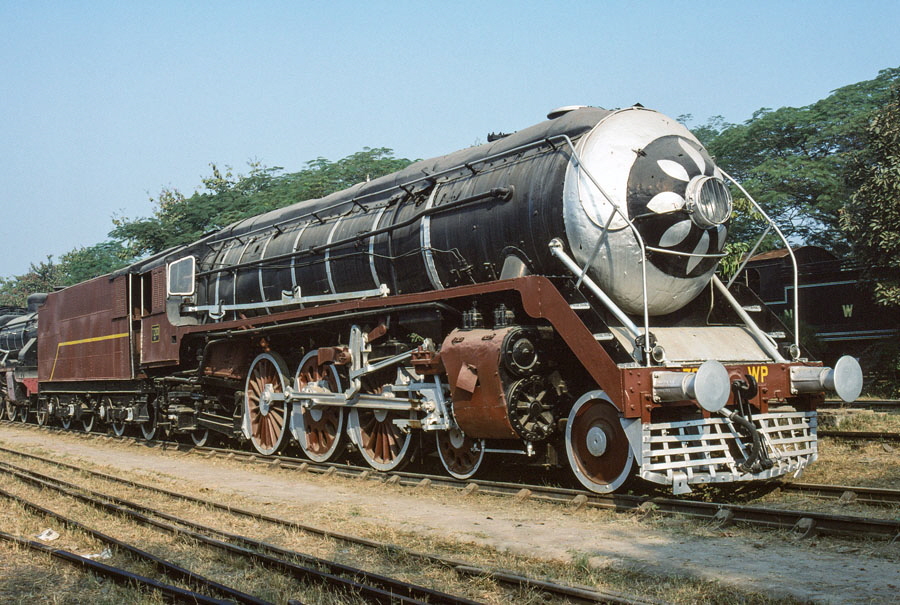

3-of-12) Broad gauge, prototype class WP/P 4-6-2 7200.
This was the first of the prototype batch, built by Baldwin in the U.S.A in 1947, of what would become the huge WP class of broad gauge express passenger locomotives. Many more were manufactured in India.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
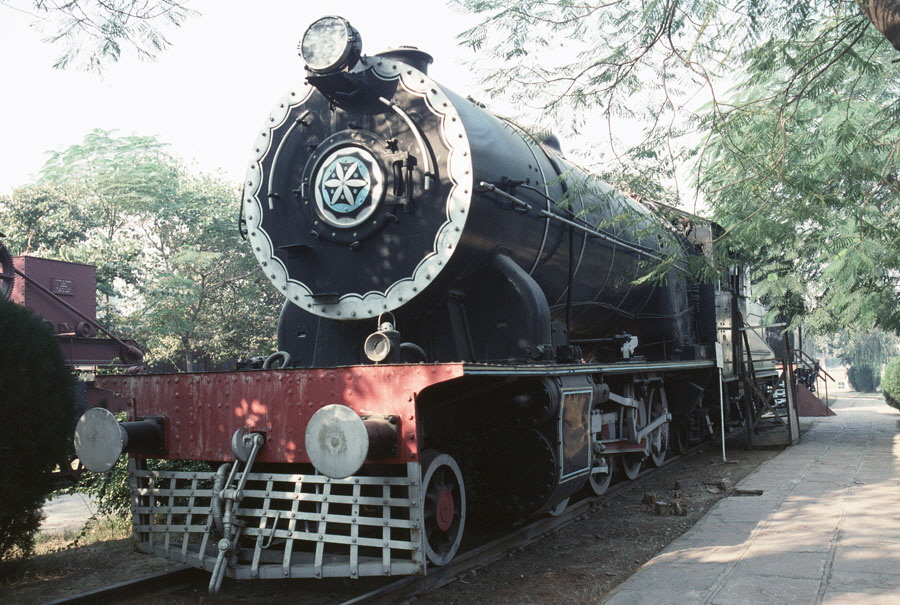

4-of-12) Broad gauge, class XG/M 2-8-2 no. 911.
The three locomotives of the XG/M class were originally built as class XG 0-8-0 by Beyer Peacock in 1928 for the North Western Railway. In 1942/3 they were converted to 2-8-2 to ease the axle load. No. 911 was used for shunting in hump marshalling yards.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
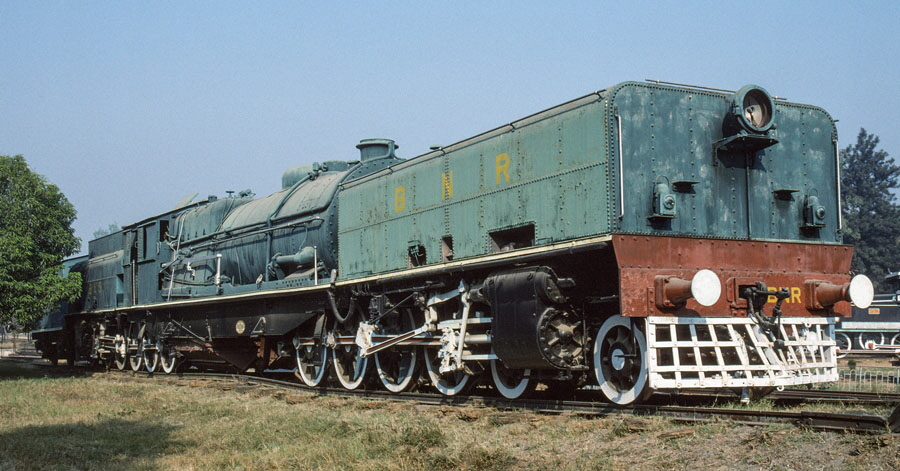

5-of-12) Broad gauge, class N "Beyer-Garratt" 4-8-0+0-8-4 815.
These locomotives were built in 1930 by Beyer-Peacock to haul heavy coal trains on steeply graded routes of the Bengal-Nagpur Railway and were the largest steam locomotives used in India.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
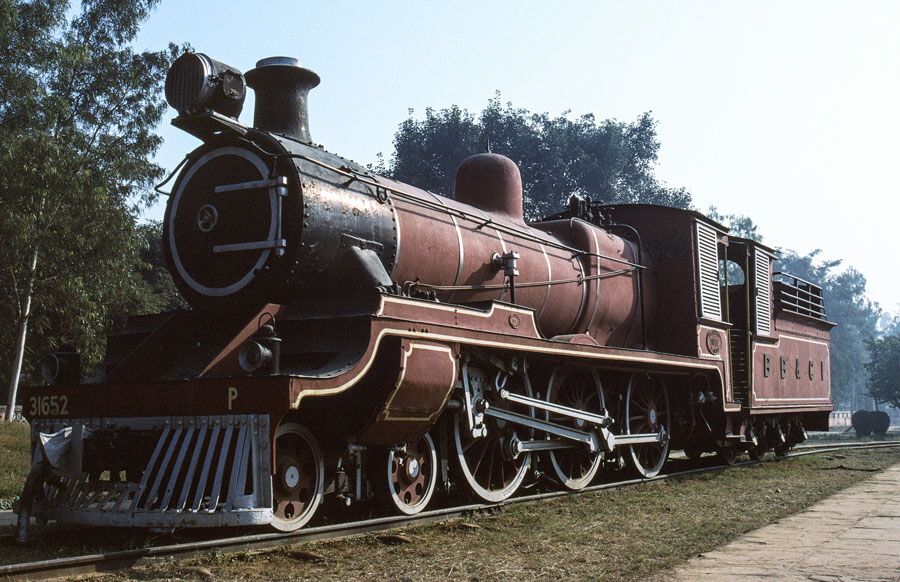

6-of-12) Metre gauge, class P 4-6-0 31652.
This locomotive, based on the standard BESA (British Engineeringing Standards Association) express passenger design, was built at the Ajmer works of the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway in 1922.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
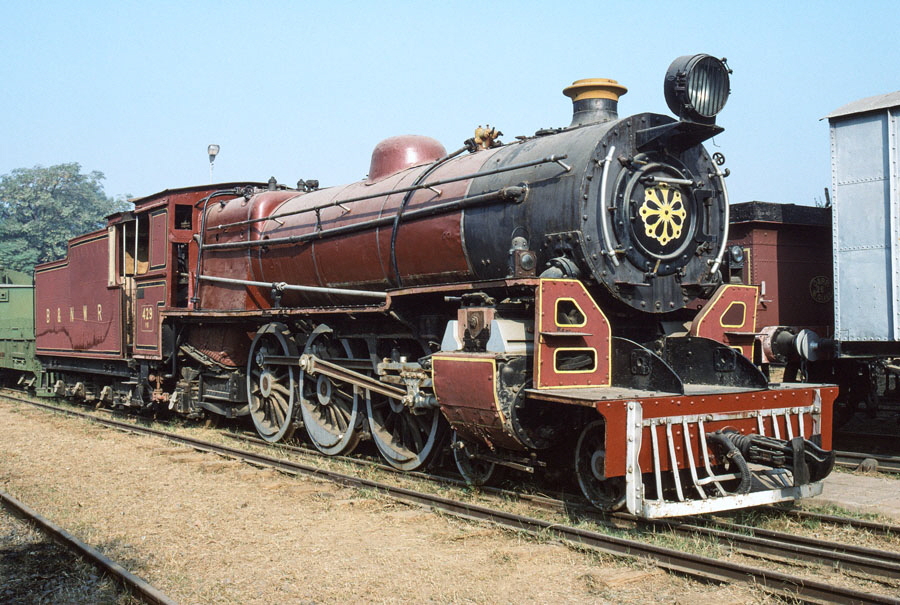

7-of-12) Metre gauge, IRS (Indian Railway Standard) class YB/2 4-6-2 429.
This locomotive was built by Nasmyth Wilson in 1935 for the Bengal and North Western Railway.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
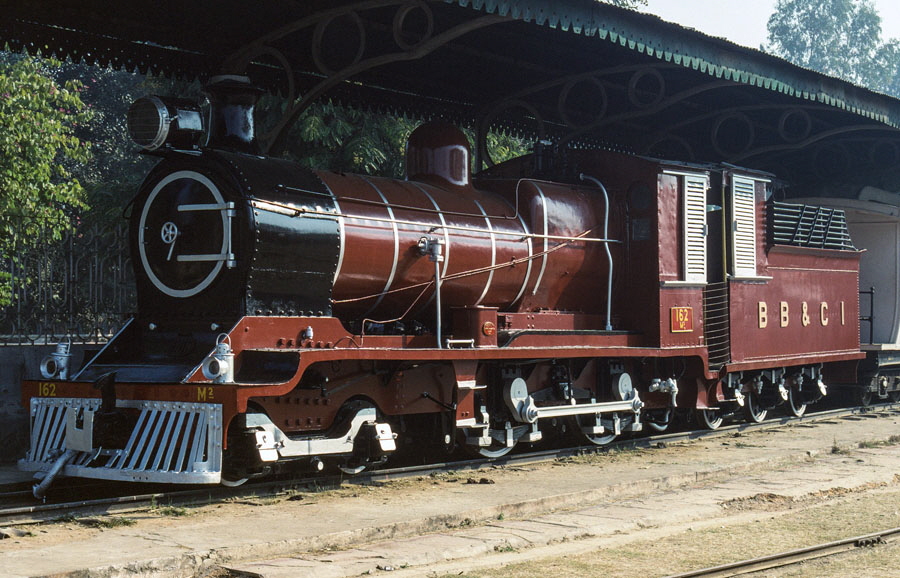
8-of-12) Metre gauge, class M2 4-4-0 162 at the National Railway Museum, Delhi, India, 26th December 1993.
This locomotive, was built at the Ajmer works of the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway in 1923.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
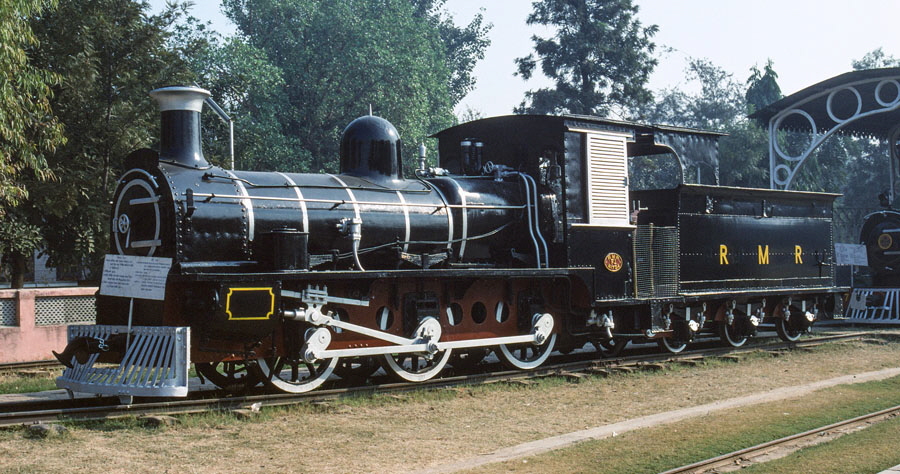

9-of-12) Metre gauge, class F1 0-6-0 734.
This was the first locomotive to be built entirely in India. It was built at the Ajmer works of the Rajputana Malwa Railway in 1895 (this railway was at the time leased to the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway, before being incorporated in it). A number of locomotives of this type were sent to the middle east during both WWI and WWII.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
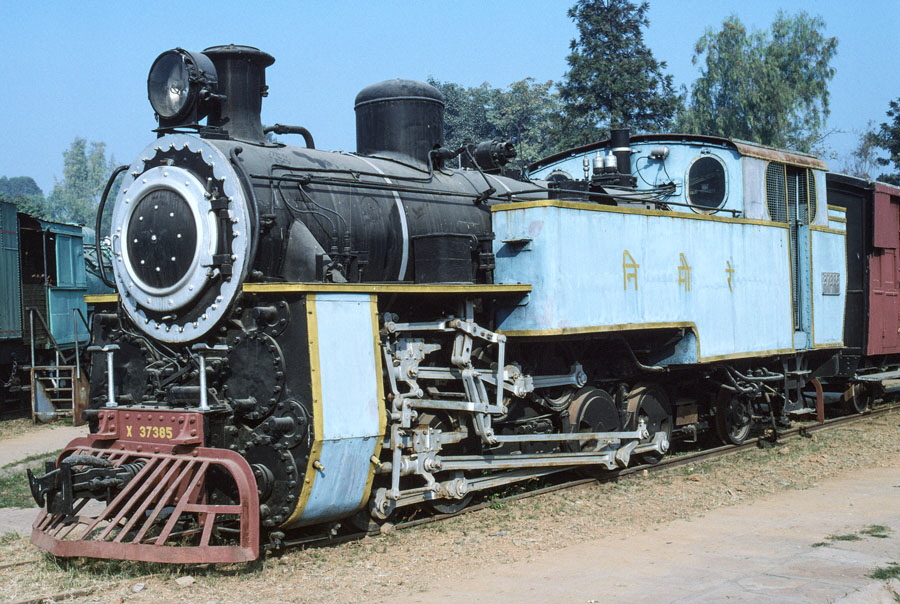

10-of-12) Metre gauge, class X 0-8-2T 37385 from the Nilgiri rack railway.
This locomotive operates using the Abt rack-and-pinion system to climb the mountainous Nilgiri railway. It was built at SLM (Swiss Locomotive and Machine Works) in 1920 and is a compound locomotive; the high pressure cylinders drive onto the normal wheels and the low pressure, upper, cylinders drive the rack wheels.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
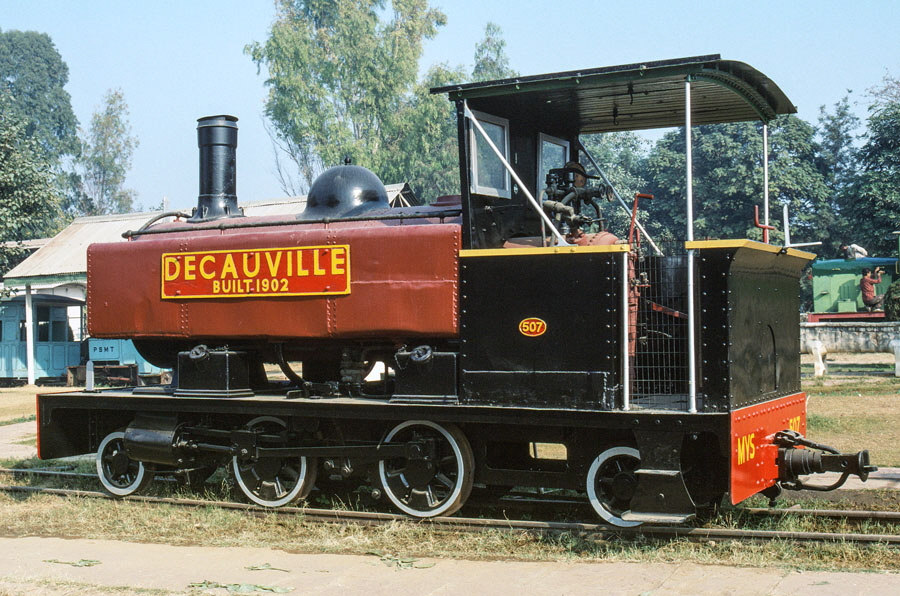

11-of-12) 2’ 6” gauge, 2-4-2T 507 (built by Bagnall in 1902).
This locomotive was used on strategic military railways in the North West Frontier. These railways used the Decauville system of prefabricated panels of track which could be easily taken up and relaid as required.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
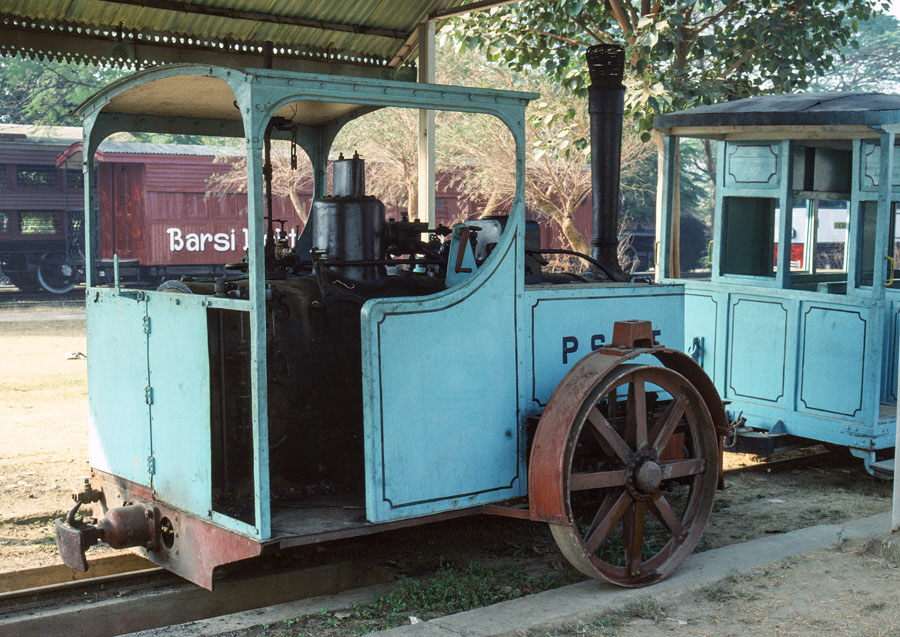

12-of-12) Patiala State Monorail 0-3-0T (built by Orenstein and Koppel in 1909) and reconstructed Chief Engineer's private inspection car.
This unusual monorail utilised the Ewing system. Here the rolling stock used double-flanged wheels to locate the vehicles on the single rail together with a balancing wheel which ran along the ground on one side. The monorail was operational from 1907 till it was abandoned due to motor competition in 1927.
Click here for a high-resolution image.
This photograph is available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
![]() Many of the photographs in these railway photograph galleries are available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.
Many of the photographs in these railway photograph galleries are available for use under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. Attribution should include a link to www.nigeltout.com.